Help us spread the word about melanoma prevention.
-
Be aware that not all clothing provides the same level of sun protection.
Regular summer clothes may have an Ultra Protection Factor rating (UPF) as low as 5.
A UPF of 5 provides little sun protection and lets large amounts of sunlight and UV rays pass through. This can lead to skin damage, premature skin ageing, skin cancer and melanoma. -
The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends sun protective clothing as the best way to protect your skin against the sun's damaging rays.
Solbari UPF50+ clothing, sun hats and UPF50+ accessories provide the highest sun protection rating for fabrics available in the world. -
Most individuals do not use sufficient sunscreen.
This means that we are not fully protected from the sun. On average, people only use 25%-50% of the recommended amount. The recommended amount is 5ml (approximately 1 teaspoon) for each arm, leg, body front, back and face including the neck and ears. All of this equates to a total of approximately 35ml for a full body application. -
Melanoma can also appear on areas not directly exposed to the sun.
It does not always appear as a mole. It can appear as a lump that can be confused with a pimple or an insect bite. These are called nodular melanomas. It is important that you go and see your doctor or dermatologist to get it checked out if in doubt. -
UVA rays can penetrate glass windows.
Make sure you protect your skin with sun protective clothing or sunscreen if you sit behind a window and close the blind if possible in peak hours of sunlight (10am-4pm). -
Early detection saves lives.
Regular skin checks with a skin doctor or dermatologist increase your chances of catching the development of skin cancer or melanoma at its earliest stage. Ideally, you are able to keep a digital record of your skin so that you can monitor any changes in your moles visit after visit and your skin lesions.
Dermatologists have developed the following ABCD guide for assessing whether or not a mole or other lesion may be becoming cancerous.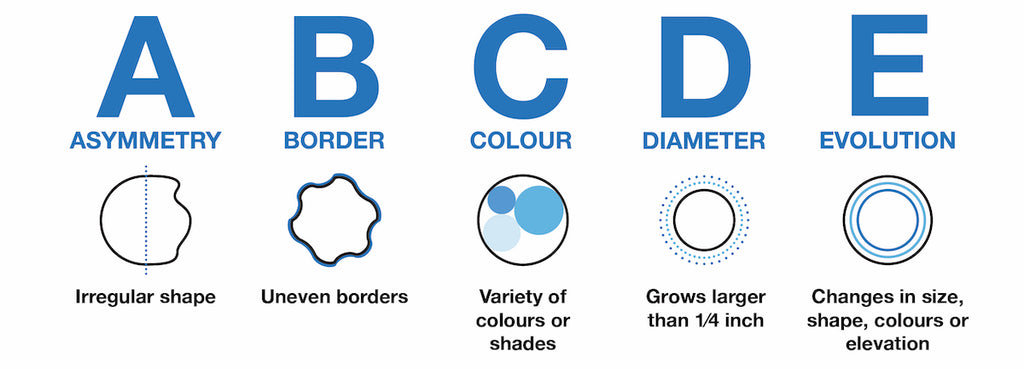
- Asymmetry: Half the mole does not match the other half in size, shape or colour.
- Border: The edges of moles are irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined.
- Colour: The mole is not the same colour throughout.
- Diameter: The mole is usually greater than 6 millimetres when diagnosed, but may also be smaller.
- Evolution: A mole or skin lesion that is different from the rest, or changes in size, shape, or colour.
If any of these conditions occur, please make an appointment to see your skin doctor or dermatologist as soon as possible. The doctor may do a biopsy of the mole to determine if it is or isn't cancerous.
You can find out more about Solbari's sun protective range by clicking the links below:
Women UPF 50+
Men UPF 50+
Sun hats UPF 50+
Accessories UPF 50+
SPF 50+ Sunscreen
Content Disclaimer: This website provides general information about medicine, health and related subjects. All content and media on the Solbari website is created and published online for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice and should not be relied on as health or personal advice. If the reader or any other person has a medical concern, he or she should seek professional advice.



